Location-Based Services (LBS): How Your Phone Knows Where You Are
5 min read
30 Jul 2024
Location-Based Services (LBS) utilize the geographic position of a mobile device to provide personalized information, navigation, and social networking services. This article explores the applications, technologies, benefits, challenges, and future trends of LBS.
Applications of Location-Based Services
Navigation and Mapping: Providing real-time directions, traffic updates, and points of interest based on the user's current location.
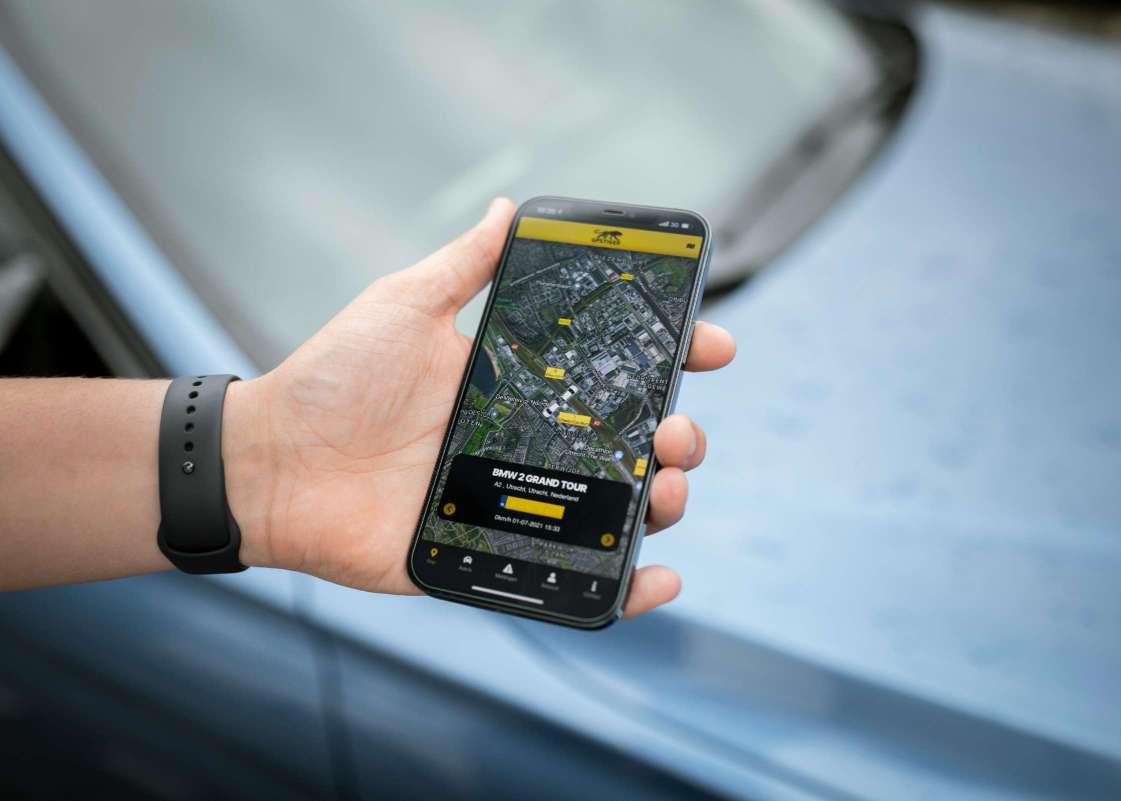

Location-Based Advertising: Delivering targeted ads and promotions to users based on their proximity to businesses, events, or specific geographic areas.
Social Networking: Facilitating location-sharing, check-ins, and proximity-based networking among users of social media platforms.
Technologies Behind LBS
Global Positioning System (GPS): Utilizing satellite signals to determine precise geographic coordinates of a mobile device anywhere on Earth.
Wi-Fi Positioning System (WPS): Using Wi-Fi access points to estimate a device's location based on signal strength and proximity to known Wi-Fi networks.
Cellular Triangulation: Determining location by measuring the signal strength and timing of radio signals from nearby cell towers.
Benefits and Impact
Enhanced User Experience: Improving usability of mobile applications with personalized recommendations, location-aware notifications, and contextual information.
Business Insights: Gaining valuable consumer behavior data, foot traffic analysis, and location-based analytics for targeted marketing strategies.
Emergency Services: Assisting emergency responders in locating individuals in distress and providing accurate location information during emergencies.
Challenges and Considerations
Privacy Concerns: Addressing user privacy issues related to location tracking, data collection, and the sharing of location information with third-party services.
Accuracy and Reliability: Overcoming challenges in urban environments, indoor spaces, and remote areas where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to regional regulations and guidelines for data protection, consent requirements, and location-based advertising practices.
Future Trends in Location-Based Services
Augmented Reality (AR): Integrating location-based data with AR applications for immersive experiences, indoor navigation, and interactive storytelling.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Connecting LBS with IoT devices for smart home automation, asset tracking, and personalized services based on real-time sensor data.
5G Connectivity: Leveraging high-speed 5G networks for faster data transmission, reduced latency, and enhanced accuracy in location-based applications.
Conclusion
Location-Based Services continue to evolve, leveraging advances in technology to enhance user experiences, support business strategies, and improve safety and efficiency across various sectors. As LBS capabilities expand and integrate with emerging technologies, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of digital interactions and connected environments.
More Articles

Emerging Trends in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
7 min read | 04 Jun 2024

Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Development
5 min read | 03 Jun 2024

Tech for Good: Innovations Driving Social Impact
4 min read | 02 Jun 2024

Cybersecurity Trends: Staying Ahead of Emerging Threats
4 min read | 01 Jun 2024
More Articles

AI and Cybersecurity: Defending Against Emerging Threats
5 min read | 10 Jul 2024

The Impact of AI on Employment: Challenges and Opportunities
3 min read | 09 Jul 2024

AI Ethics: Addressing Bias and Responsible AI Development
4 min read | 08 Jul 2024
Computer Vision: Applications and Innovations in AI
3 min read | 07 Jul 2024
