3D Printing: How It's Changing the World as We Know It
7 min read
17 Jul 2024
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing various industries by enabling the creation of complex objects layer by layer from digital designs. This article explores the transformative impact of 3D printing, its applications across different sectors, and its potential to reshape manufacturing and innovation.
Understanding 3D Printing
Layered Manufacturing: Building objects by depositing materials layer by layer, guided by digital blueprints or CAD models.
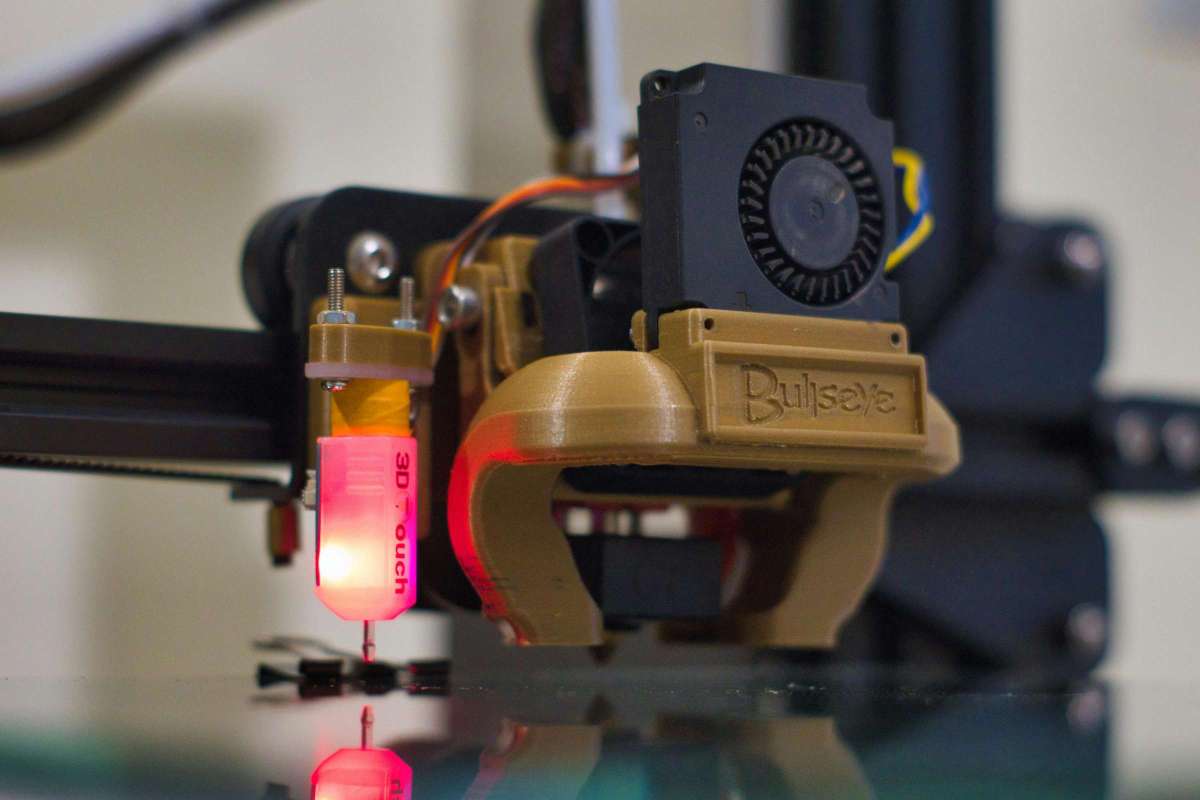
Material Options: Utilizing a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, to achieve diverse functionalities and properties.
Printing Processes: Employing techniques such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and binder jetting to create precise, customized parts.
Post-Processing: Finishing printed objects through processes like curing, polishing, or painting to meet specific requirements.
Applications Across Industries
Healthcare: Producing personalized medical devices, prosthetics, and implants tailored to individual patient needs.
Automotive: Rapid prototyping of vehicle parts, tooling, and components for testing and production optimization.
Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight, complex aircraft components, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
Consumer Goods: Customizing products such as jewelry, fashion accessories, and home décor items with intricate designs and textures.
Impact on Manufacturing and Innovation
Speed and Efficiency: Accelerating product development cycles and reducing time-to-market through rapid prototyping and on-demand production.
Design Freedom: Empowering designers to explore creative designs and geometries that were previously impossible or costly to produce.
Sustainability: Minimizing material waste and energy consumption compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Localized Production: Facilitating decentralized manufacturing and reducing reliance on global supply chains.
Challenges and Considerations
Material Limitations: Overcoming challenges related to material properties, durability, and performance in specific applications.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistent quality and reliability of printed parts through rigorous testing and validation processes.
Regulatory Compliance: Addressing regulatory requirements and standards for safety, quality, and environmental impact.
Future Outlook
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve with advancements in materials science, printing processes, and software capabilities, its adoption across industries is expected to grow. With ongoing innovation and integration into manufacturing workflows, 3D printing is poised to drive new levels of customization, efficiency, and sustainability in the global economy.
More Articles

Can Blockchain Power a More Democratic Future?
4 min read | 05 Aug 2024

Will Blockchain Make Banks Obsolete?
7 min read | 04 Aug 2024

Blockchain for Social Impact: Solving Global Challenges with Distributed Ledgers
7 min read | 03 Aug 2024
DAOs: Redefining Governance with Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
5 min read | 02 Aug 2024
More Articles

AI in Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to Individual Patients
7 min read | 22 Aug 2024

The Future of Quantum Computing and Its Impact on AI
5 min read | 21 Aug 2024
AI and Blockchain: The Potential for Secure and Transparent Systems
7 min read | 20 Aug 2024

AI in Smart Cities: Improving Urban Living with Intelligent Systems
4 min read | 19 Aug 2024
